What is Herniated Disk, symptoms and treatment
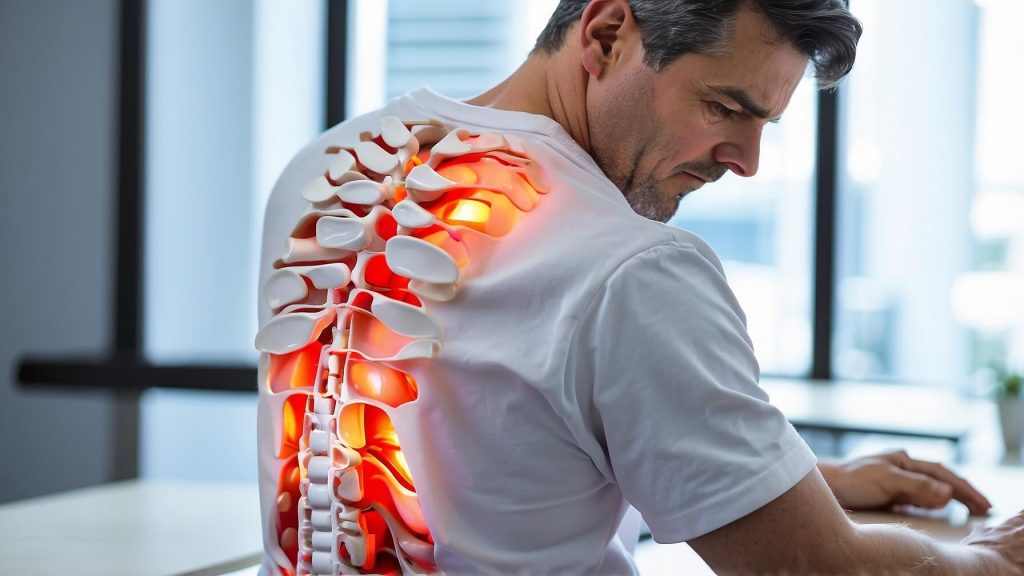
The pain and discomfort of a herniated disc can greatly affect your quality of life.
Here is what you need to know about herniated discs, including what they are, their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment. In addition, learn about medications, self-care, surgery, and lifestyle options to help relieve pain.
What is a herniated disk?
The Cleveland Clinic describes a herniated disc as a spinal cord injury. The spinal cord is made up of bony parts called vertebrae, and between the vertebrae are intervertebral discs that act as cushions. The discs make it easier to bend and move. When a disc tears or leaks, it is called a herniated disc. A herniated disc usually occurs in the lower back or neck area. A herniated disc is also called a slipped disc, ruptured disc, or bulging disc.
Herniated disk causes and risk factors
- Herniated discs often occur with age. The Mayo Clinic lists the following risk factors
- Weight: Excessive weight puts strain on the lower back.
- Occupation: People who have physically demanding jobs that involve repetitive lifting, pulling, pushing, or bending are more likely to have herniated discs.
- Genetics
- Smoking: Smoking decreases the oxygen supply to the disc and is thought to cause the disc to break down more quickly.
- Frequent driving: prolonged sitting puts strain on the spine.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
Herniated disk symptoms
- Penn Medicine lists the following symptoms of a herniated disk:
- Pain on one side of the body
- Sharp pain in part of the leg, buttock, or hip
- Numbness in part of the leg, back of the calf or foot
- Muscle weakness on one side of the leg
- Pain when moving the neck
- Deep pain near or above the shoulder blade
- Pain that moves along the arm Worse after sitting or standing, at night, sneezing, coughing, laughing, walking more than a few meters, or bending backward
Herniated disk diagnosis
The health care provider may examine pain, muscle reflexes, sensation, and muscle strength and order diagnostic tests such as
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): most common and accurate method of examining a herniated disc.
- X-ray: helps rule out other causes.
- Computed tomography (CT): to view the condition of the bones of the spine: a test to look at the condition of the bones of the spine.
- Myelography: dye is injected into the spinal cord to locate a herniated disc.
- Electromyography (EMG): to evaluate nerve function.
Herniated disk treatment
Dr. Mark Wang, an orthopedic spine surgeon at Desert Institute for Spinal Care in Phoenix, writes, “Doctors prefer nonsurgical treatment over surgery whenever possible. If surgery is necessary, they will consider your condition and opt for the least invasive option that has the best chance of success.”
Wang lists several non-surgical treatment options:
- Physical Therapy: May include heat and cold therapy.
- Heat and cold therapy: Cold therapy reduces inflammation and pain; heat therapy promotes circulation and healing.
- Alternative therapies: Acupuncture and chiropractic may be helpful.
- Selective nerve root block: A minimally invasive steroid anesthetic injection that blocks pain signals between the spinal nerves and the brain.
- Epidural steroid injection: Injects medication into the epidural space of the spinal column.
The Mayo Clinic lists several medications for herniated disks:
- Nonprescription analgesics: acetaminophen (Tylenol), ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), naproxen sodium (Aleve) for mild to moderate pain.
- Neuropathic drugs: gabapentin (Glarisse, Horizont, Neurontin), pregabalin (Lyrica), duloxetine (Cymbalta, Drysalma Sprinkle), venlafaxine (Effexor XR).
- Muscle relaxants: reduce spasms.
- Opioids: considered when other medications do not work because of the risk of addiction and side effects.
There are several types of herniated disc surgery, Wang noted. They include:
- Microdiscectomy: Minimally invasive surgery to remove a portion of the disc that is causing pain. The disc may be repaired by re-inflating it with hyaluronic acid and sealing it with collagen.
- Lumbar laminectomy: Minimally invasive or open surgery in which a portion of the vertebrae (lamina) is removed to relieve pressure on the spinal cord and nerve roots.
- Spinal fusion: a surgeon fuses two or more bones of the spine together. This may limit mobility, but is effective in reducing painful movement of the spine.
- Artificial disc replacement or artificial cervical disc replacement: The affected disc is replaced with a metal or plastic one.
- Endoscopic discoplasty: relieves pain by freeing the nerves in the intervertebral foramen (the hollow bony tunnel through which spinal nerves exit the arms and legs).
Living with a herniated disk
If symptoms are present, seek the advice of a health care professional. Early treatment can prevent further problems. According to the American Academy of Family Physicians, most people feel better in about four weeks.
Herniated disk self-care
Self-care for a herniated disk includes some lifestyle changes:
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Avoid sitting or standing for long periods of time
- Wear flat shoes, not high heels
- Keep objects close to your body







Comment